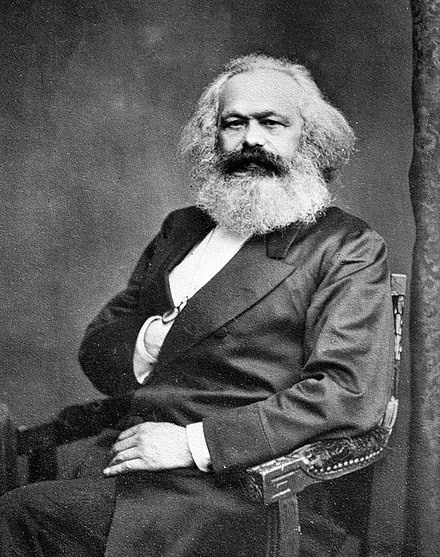
Karl Marx (1818-1883) was a German philosopher, economist, and political theorist who is best known for his influential theories on socialism, communism, and the relationship between labor and capital. His ideas have had a profound impact on politics, economics, and social theory, and continue to be studied and debated to this day.
Marx was born in Trier, Germany, and studied law and philosophy at the University of Berlin. He later moved to Paris, where he became involved in revolutionary politics and met Friedrich Engels, who would become his lifelong collaborator and friend.
Together, Marx and Engels wrote and published several influential works, including the Communist Manifesto, which laid out their vision for a socialist society. They also worked on a monumental study of capitalism, which was published after Marx’s death under the title “Das Kapital.”
Marx’s theories emphasized the importance of economic and social structures in shaping human behavior and relationships. He argued that capitalism was inherently exploitative, and that workers were alienated from their labor and from one another under this system. Marx believed that the only way to achieve true equality and freedom was through a socialist revolution, in which workers would seize control of the means of production and establish a classless society.
Marx’s ideas had a significant impact on socialist and communist movements around the world, and his theories continue to be influential in many fields of study, including economics, political science, and sociology. Although his ideas have been controversial and have led to many different interpretations, Marx remains one of the most important and influential thinkers in modern history.









Leave a comment