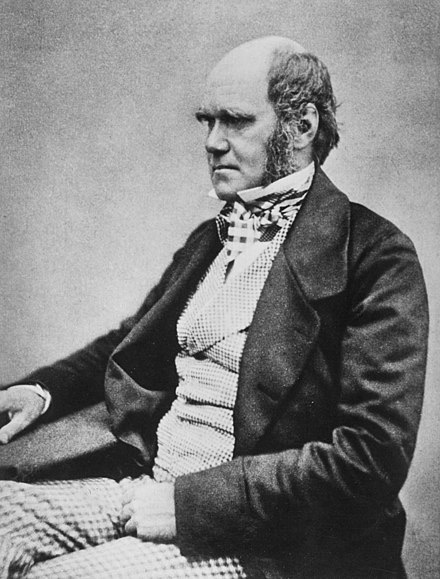
Charles Darwin (1809-1882) was an English naturalist and biologist who is best known for his theory of evolution and the concept of natural selection. His ideas on the origin of species challenged the prevailing beliefs of his time and have had a profound impact on the field of biology.
Darwin was born in Shrewsbury, England, and showed an early interest in natural history. He studied at the University of Edinburgh and later at Christ’s College, Cambridge. In 1831, Darwin embarked on a five-year voyage aboard the HMS Beagle, during which he collected specimens and made observations that would inform his later work.
Upon his return to England, Darwin began to develop his theory of evolution. In 1859, he published “On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection,” which laid out his argument for the process by which species change over time through natural selection. This theory was controversial at the time, as it challenged the traditional belief in divine creation and the idea that species were unchanging.
Darwin continued to conduct research and publish works on evolution, including “The Descent of Man” and “The Expression of the Emotions in Man and Animals.” He also made significant contributions to the study of geology, botany, and zoology.
Throughout his life, Darwin faced criticism and opposition from those who disagreed with his ideas. However, his theories have since been widely accepted and have revolutionized the field of biology. Darwin’s work continues to be studied and debated by scientists and scholars to this day, and he is widely regarded as one of the most influential thinkers in the history of science.









Leave a comment